记录 BFS 的算法实现
算法
A* (A star 启发式搜索)算法
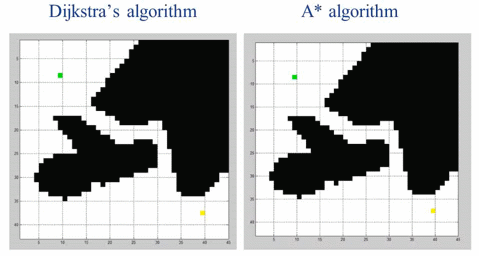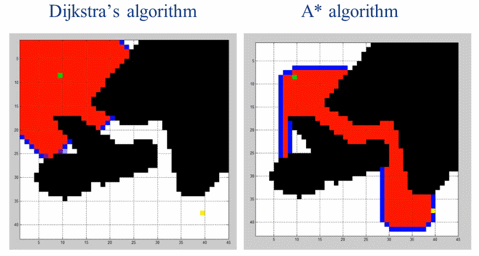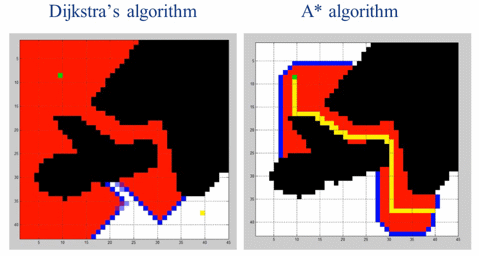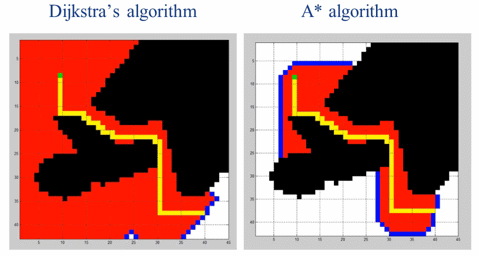
A*算法是在 BFS 基础上增加一个优化参数(Cost 代价值),这样可以减少无效遍历,更快逼近目标。
-
算法思想:
- BFS 可以逐步在网格地图中找到目标,缺点是对各方向无差别遍历造成很大浪费;
Dijkstra 可以在图中依照距离优先查找较近的目标,但如果是网格地图这种相邻结点无差别的情况下和 BFS 遍历路径是一样的,效率较低。
A*结合了网格 BFS 和 Dijkstra,适用于网格中已知起点和目标点的情况, 对每个当前位置除了维护一个距离外还有一个”额外成本”,这个”额外成本”通常是”当前点到目标点”的距离,按照综合距离进行 Dijkstra 运算综合距离 = 当前距离+额外成本
- BFS 可以逐步在网格地图中找到目标,缺点是对各方向无差别遍历造成很大浪费;
Dijkstra 可以在图中依照距离优先查找较近的目标,但如果是网格地图这种相邻结点无差别的情况下和 BFS 遍历路径是一样的,效率较低。
A*算法也叫做启发式搜索算法,其中计算当前点到目标点的函数f(cur, target)称作启发函数A*除了用于二维网格外,其实可以用于各种维度的 BFS-
通常用某种距离(广义的空间中)作为启发函数
- 欧几里得距离(欧式距离) \(f((a1,b1),(a2,b2)) = \sqrt{((a1-a2)^2 + (b1-b2)^2)}\)
- 曼哈顿距离 \(f((a1,b1),(a2,b2)) = \left|a1-a2\right|+\left|b1-b2\right|\)
- 因为计算时无需开方效率较高,在
A*中一般用曼哈顿距离
-
关于时间复杂度:
- 最大时间复杂度为
O(nlogn),其中 n 为网格数量 - 在网格路径搜索中,启发式搜索算法要明显好于 BFS 和 Dijkstra,上面的时间复杂度只能做参考
- 最大时间复杂度为
-
由于
A*算法在实际应用中效率很高,所以常用于游戏地图中的寻路算法 A*并不适合所有场景,如果在搜索过程中存在空间虫洞(位置可以快速回退),那么第一次找到目标的循环未必是最小步数。 调整启发函数策略后,可能减少问题发生概率。如:”909. Snakes and Ladders”
示例: “752. Open the Lock”
题目
“752. Open the Lock”
// BFS
func openLock(deadends []string, target string) int {
if target == "0000" {
return 0
}
tarBytes := [4]byte{target[0],target[1],target[2],target[3]}
deadSet := make(map[[4]byte]bool, len(deadends))
for _, s := range deadends {
if "0000" == s {
return -1
}
deadSet[[4]byte{s[0],s[1],s[2],s[3]}] = true
}
memSet := map[[4]byte]bool{[4]byte{'0','0','0','0'}:true}
queue := []ele{ele{value:[4]byte{'0','0','0','0'}, dist:0}}
for len(queue) > 0 {
cur := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
if cur.value == tarBytes {
return cur.dist
}
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
for j := -1; j < 2; j += 2 {
tmp := cur.value
tmp[i] += byte(j)
if tmp[i] > '9' {
tmp[i] = '0'
} else if tmp[i] < '0' {
tmp[i] = '9'
}
if deadSet[tmp] || memSet[tmp] {
continue
}
memSet[tmp] = true
queue = append(queue, ele{value:tmp, dist: cur.dist+1})
}
}
}
return -1
}
type ele struct {
value [4]byte
dist int
}
// A*
type astar struct {
g, h int
status string
}
type hp []astar
func (h hp) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h hp) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i].g+h[i].h < h[j].g+h[j].h }
func (h hp) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *hp) Push(v interface{}) { *h = append(*h, v.(astar)) }
func (h *hp) Pop() interface{} { a := *h; v := a[len(a)-1]; *h = a[:len(a)-1]; return v }
// 计算启发函数
func getH(status, target string) (ret int) {
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
dist := abs(int(status[i]) - int(target[i]))
ret += min(dist, 10-dist)
}
return
}
func openLock(deadends []string, target string) int {
const start = "0000"
if target == start {
return 0
}
dead := map[string]bool{}
for _, s := range deadends {
dead[s] = true
}
if dead[start] {
return -1
}
get := func(status string) (ret []string) {
s := []byte(status)
for i, b := range s {
s[i] = b - 1
if s[i] < '0' {
s[i] = '9'
}
ret = append(ret, string(s))
s[i] = b + 1
if s[i] > '9' {
s[i] = '0'
}
ret = append(ret, string(s))
s[i] = b
}
return
}
type pair struct {
status string
step int
}
h := hp0
seen := map[string]bool{start: true}
for len(h) > 0 {
node := heap.Pop(&h).(astar)
for _, nxt := range get(node.status) {
if !seen[nxt] && !dead[nxt] {
if nxt == target {
return node.g + 1
}
seen[nxt] = true
heap.Push(&h, astar{node.g + 1, getH(nxt, target), nxt})
}
}
}
return -1
}
“847. Shortest Path Visiting All Nodes”
func shortestPathLength(graph [][]int) int {
// 当前下标(4bit) + 状态(12bit) + 当前距离(8bit)
const STATE_MASK = 0b11111111111100000000
const DISTANCE_MASK = 0b11111111
n := len(graph)
targetMask := ((1<<n) - 1)<<8
m := make(map[int]bool, n)
q := make([]int, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
next := (i<<20)|(1<<(i+8))
q[i] = next
m[next] = true
}
for len(q) > 0 {
cur := q[0]
q = q[1:]
idx, curMask, dist := cur>>20, cur&STATE_MASK, cur&DISTANCE_MASK
if curMask == targetMask {
return dist
}
for _, next := range graph[idx] {
nextMask := (next<<20)|((1<<(next+8))|curMask)
if !m[nextMask] {
q = append(q, nextMask|(dist+1))
m[nextMask] = true
}
}
}
return 0
}
“1036. Escape a Large Maze” Golang
func isEscapePossible(blocked [][]int, source []int, target []int) bool {
blockMap := make(map[Point]struct{})
for _, b := range blocked {
blockMap[Point{b[0], b[1]}] = struct{}{}
}
return bfs(Point{source[0], source[1]}, Point{target[0], target[1]}, blockMap) && bfs(Point{target[0], target[1]}, Point{source[0], source[1]}, blockMap)
}
type Point [2]int
func bfs(source Point, target Point, block map[Point]struct{}) (ret bool) {
dir := [][]int{ {-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1} }
visited := map[Point]struct{}{source:struct{}{}}
l := list.New()
l.PushBack(source)
steps := 0
for l.Len() > 0 && steps < 20000 {
cur := l.Remove(l.Front()).(Point)
steps++
if cur == target {
return true
}
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
next := Point{cur[0]+dir[i][0], cur[1]+dir[i][1]}
if next[0] < 0 || next[1] < 0 || next[0] >= 1e6 || next[1] >= 1e6 {
continue
} else if _, exists := block[next]; exists {
continue
} else if _, exists := visited[next]; exists {
continue
}
visited[next] = struct{}{}
l.PushBack(next)
}
}
if steps >= 20000 {
return true
}
return false
}