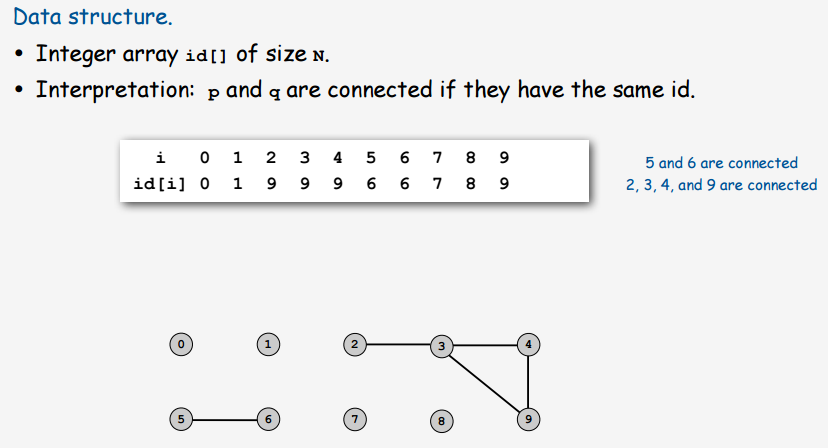
数据结构特性
并查集,DSU(Disjoint Set Union),对应的算法也叫 Union Find。
该数据结构用于将有关联的元素合并为多个集合,使用非常简单、实现逻辑也不复杂。
对数据进行紧密排列处理(将离散数据紧密排列后添加 id)后空间复杂度 O(n),时间复杂度 O(n),性能非常好。
- 有些情况下,元素并不是紧密排列的,而是比较稀疏的,比如[0~1e9]之内的 1000 个元素。 这时需要利用”Array+hashMap”的方式对元素进行”重排”,变为排列紧密的数据后,再利用 DSU 处理
数据结构的实现
// C++版本
class DSU{
private:
vector<int> parent_; // 用于集合关联,默认每个元素自己是一个集合。
vector<int> rank_; // 将孩子较少的节点合并到节点较多的节点,减少查找次数。
public:
DSU(int N) {
parent_.resize(N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) // 每个元素默认是自己的集合的根
parent_[i] = i;
rank_.resize(N, 1); // rank默认数为1
}
int find(int x) { // 每次查找,都递归进行合并,避免层数过高。
if (parent_[x] != x)
parent_[x] = find(parent_[x]);
return parent_[x];
}
int find(int x, int &outSize) { // 可以查找当前集合总数
if(parent_[x] != x) parent_[x] = find(parent_[x]);
outSize = rank_[parent_[x]];
return parent_[x];
}
bool doUnion(int x, int y) {
int xr = find(x), yr = find(y);
if(xr == yr)
return false;
else if (rank_[xr] < rank_[yr]) {
parent_[xr] = yr;
rank_[yr] += rank_[xr];
} else {
parent_[yr] = xr;
rank_[xr] += rank_[yr];
}
return true;
}
};
// Go 版本
type DSU struct {
parents []int
ranks []int
}
// 创建DSU对象
func NewDSU(size int) (res *DSU) {
if size <= 0 {
return
}
res = &DSU{
parents : make([]int, size),
ranks : make([]int, size),
}
for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
res.parents[i] = i
res.ranks[i] = 1
}
return
}
func (p *DSU) Find(x int) (root int, err error) {
if x < 0 || x >= len(p.parents) {
err = errors.New("invalid index")
return
}
if p.parents[x] != x {
p.parents[x], _ = p.Find(p.parents[x])
}
root = p.parents[x]
return
}
func (p *DSU) Union(x ,y int) (res bool, err error) {
if x < 0 || x >= len(p.parents) || y < 0 || y >= len(p.parents) {
err = errors.New("invalid index")
return
}
xRoot, _ := p.Find(x)
yRoot, _ := p.Find(y)
if xRoot == yRoot {
res = false
return
}
if p.ranks[xRoot] >= p.ranks[yRoot] {
p.parents[yRoot] = xRoot
p.ranks[xRoot] += p.ranks[yRoot]
} else {
p.parents[xRoot] = yRoot
p.ranks[yRoot] += p.ranks[xRoot]
}
res = true
return
}
应用示例
此题目来自于 leetcode”399. Evaluate Division”,该题目有两种解法,一种是 DFS 搜索除法关系链,一种是下面这种 DSU 解法。后者在时间复杂度上有明显优势,每一次查找是 O(1)。
/*
challenge:
Equations are given in the format A / B = k, where A and B are variables represented as strings,
and k is a real number (floating point number). Given some queries, return the answers.
If the answer does not exist, return -1.0.
Example:
Given a / b = 2.0, b / c = 3.0.
queries are: a / c = ?, b / a = ?, a / e = ?, a / a = ?, x / x = ? .
return [6.0, 0.5, -1.0, 1.0, -1.0 ].
The input is: vector<pair<string, string>> equations, vector<double>& values,
vector<pair<string, string>> queries , where equations.size() == values.size(),
and the values are positive. This represents the equations. Return vector<double>.
According to the example above:
equations = [ ["a", "b"], ["b", "c"] ],
values = [2.0, 3.0],
queries = [ ["a", "c"], ["b", "a"], ["a", "e"], ["a", "a"], ["x", "x"] ].
The input is always valid. You may assume that evaluating the queries will result in
no division by zero and there is no contradiction.
*/
type DSU struct {
parent map[string]string // node->parent of the node
ratio map[string]float64 // node->(node value / parent value)
}
func (p *DSU) Union(divided, divisor string, value float64) {
for _, node := range []string{divided, divisor} {
if _, exists := p.parent[node]; !exists {
p.parent[node] = node
p.ratio[node] = 1.0
}
}
p1, dividedRatio := p.Find(divided)
p2, divisorRatio := p.Find(divisor)
p.parent[p1] = p2
p.ratio[p1] = value * divisorRatio / dividedRatio
}
func (p *DSU) Find(node string) (ancestor string, ratio float64) {
ancestor, exists := p.parent[node]
if !exists {
return
}
if node == ancestor {
ratio = p.ratio[node]
return
}
father := p.parent[node]
ancestor, fatherRatio := p.Find(father)
p.parent[node] = ancestor
p.ratio[node] = p.ratio[node] * fatherRatio
ratio = p.ratio[node]
return
}
func NewDSU() *DSU {
return &DSU {
parent : make(map[string]string),
ratio : make(map[string]float64),
}
}
func calcEquation(equations [][]string, values []float64, queries [][]string) []float64 {
dsu := NewDSU()
for i := 0; i < len(equations); i++ {
dsu.Union(equations[i][0], equations[i][1], values[i])
}
res := make([]float64, 0, len(queries))
for _, q := range queries {
p1, r1 := dsu.Find(q[0])
p2, r2 := dsu.Find(q[1])
// not in dsu or not in the same set
if p1 == "" || p2 == "" || p1 != p2 {
res = append(res, -1.0)
} else {
res = append(res, r1 / r2)
}
}
return res
}